Process Incoming Data on Multiple Threads
Another way to speed up DataPipeline applications is to use multi-threading to process incoming data in parallel. This is where the AsyncTaskReader comes in. AsyncTaskReader provides a convenient facade on top of several DataPipeline classes to make parallelizing tasks a breeze. It runs the same task (a sequential set of operations) on the specified number of threads to operate on data in a divide-and-conquer fashion instead of one-at-a-time.
How to use AsyncTaskReader
A common pipeline might read from a CSV file, perform a few transformations, filters, and conversions before writing to a database.

AsyncTaskReader comes in handy when some of the steps between reading and writing can be sped up by performing them on a partition of data concurrently.
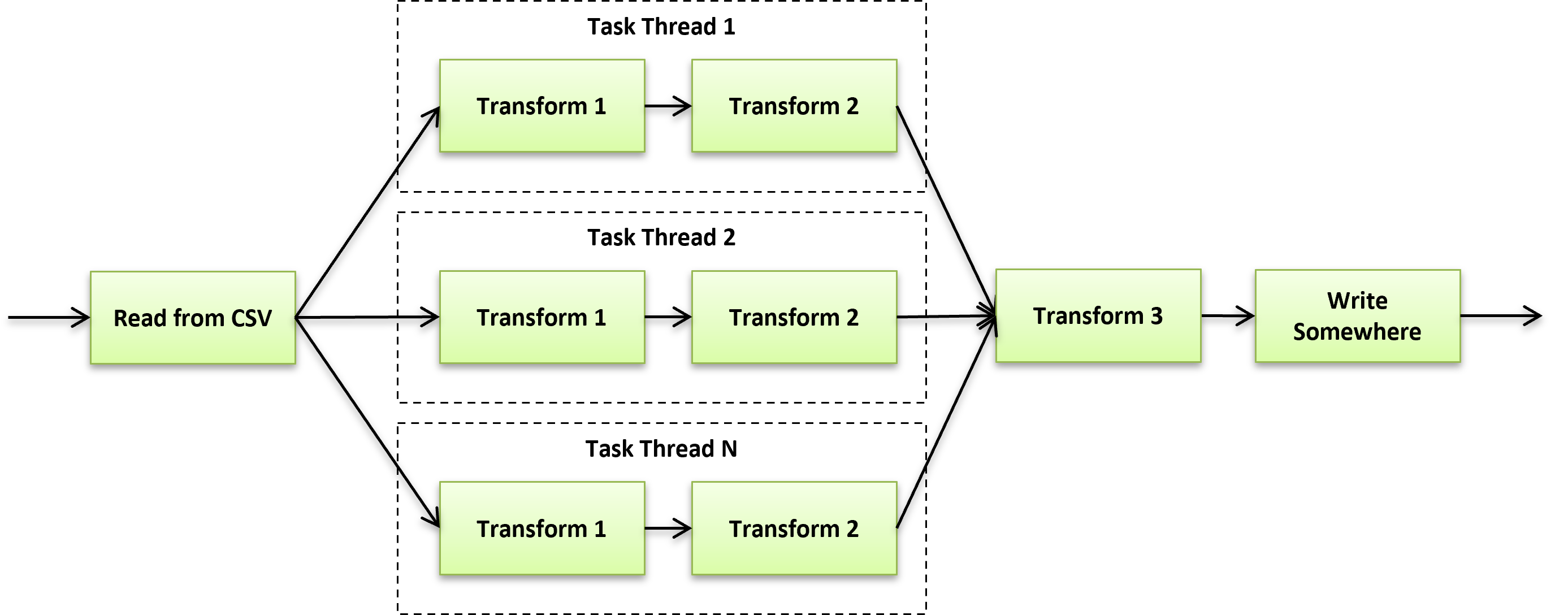
The Read And Transform Data in Parallel example below shows how to perform RenameField and BasicFieldTransformer operations using 4 threads. The key is to supply AsyncTaskReader with a DataReaderDecorator instance that will be used to apply your operations to each of the parallel pipelines.
package com.northconcepts.datapipeline.examples.cookbook;
import java.io.File;
import com.northconcepts.datapipeline.core.AsyncTaskReader;
import com.northconcepts.datapipeline.core.DataReader;
import com.northconcepts.datapipeline.core.SortingReader;
import com.northconcepts.datapipeline.core.StreamWriter;
import com.northconcepts.datapipeline.csv.CSVReader;
import com.northconcepts.datapipeline.job.DataReaderDecorator;
import com.northconcepts.datapipeline.job.Job;
import com.northconcepts.datapipeline.transform.BasicFieldTransformer;
import com.northconcepts.datapipeline.transform.RenameField;
import com.northconcepts.datapipeline.transform.TransformingReader;
public class ReadAndTransformDataInParallel {
private static final int THREADS = 4;
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataReader reader = new CSVReader(new File("example/data/input/credit-balance-02-1000000.csv"))
.setFieldNamesInFirstRow(true);
reader = new AsyncTaskReader(reader, createTaskToRunInMultipleThreads(), THREADS);
Job.run(new SortingReader(reader).add("Balance"), StreamWriter.newSystemOutWriter());
}
private static DataReaderDecorator createTaskToRunInMultipleThreads() {
return (originalDataReader) -> new TransformingReader(originalDataReader)
.add(new RenameField("Rating", "AccountRating"))
.add(new BasicFieldTransformer("Balance").stringToDouble().nullToValue(0.0));
}
}
How AsyncTaskReader Works
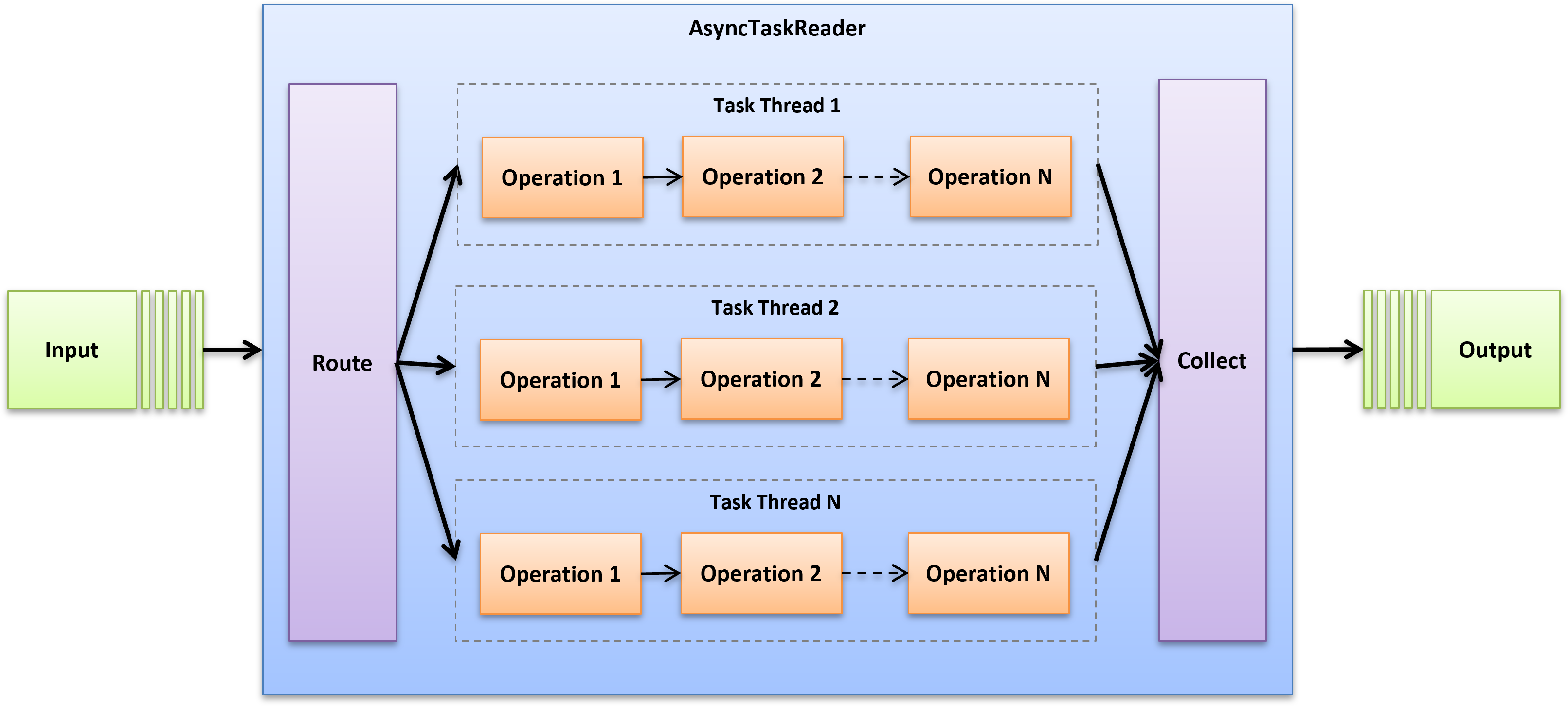
- Behind the scenes, AsyncTaskReader uses SplitWriter to divide and route the incoming data into multiple, independent streams based on the number of threads you specified.
- Each stream is decorated with your task using your instance of DataReaderDecorator. This allows it to perform identical work on the divided pipelines.
- An AsyncMultiReaderis the used to collect and merge the outgoing data from the parallel streams into a single pipeline.
- The AsyncMultiReader is set as the nested source for the outer AsyncTaskReader to supply its downstream readers.
